In a world where mental health issues are on the rise, the quest for accessible support has led to the creation of AI chatbots.
These digital companions are here to lend an ear, any time of the day. But can they replace the human touch in mental health care? Or do they offer a new form of support, enhancing our path to mental well-being?
This article delves into the world of AI chatbots for mental health, unveiling their functionality, effectiveness, and the science behind their operation.
Key Takeaways
Aspect Summary Definition AI chatbots are programmed to provide instant responses based on user input, offering support and coping strategies for mental health issues. Popular Chatbots Woebot, Youper, Elomia, ChatGPT, and Earkick are among the popular AI chatbots offering mental health support. Underlying Technologies Utilizing AI and machine learning, these chatbots employ psychological frameworks like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to interact with users. Benefits They provide accessible, instant, and stigma-free support, especially beneficial in times or areas where traditional therapy is unavailable. Concerns Privacy, effectiveness, and lack of human interaction are among the concerns surrounding AI chatbots for mental health. Future Prospects With evolving AI technology, these chatbots are poised to become more effective, offering a promising avenue for mental health support.
What Are Mental Health Chatbots?
Mental health chatbots are at the intersection of psychology and artificial intelligence, designed to provide support and therapeutic interaction.
Definition and Purpose
AI chatbots for mental health are programmed to simulate human conversation and provide immediate responses.
They are created to:
- Offer emotional support
- Provide coping strategies
- Give information on mental health issues
- Assist in crisis situations
They are accessible via smartphones or computers, making mental health support available anytime, anywhere.
Types of Mental Health Issues Addressed
These chatbots can aid in managing a variety of mental health issues including:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Stress
- Relationship problems
They utilize algorithms to provide personalized responses based on user input.
| Mental Health Issue | Chatbot |
|---|---|
| Anxiety | Woebot, Youper, Elomia, ChatGPT |
| Depression | Woebot, Youper, Elomia, ChatGPT |
| Stress | Elomia, ChatGPT, Earkick |
| Relationship problems | Elomia, ChatGPT |
| Trauma | Woebot, Elomia, ChatGPT |
| Eating disorders | Youper, Elomia, ChatGPT |
| Substance abuse | Elomia, ChatGPT |
| Bipolar disorder | Woebot, Elomia, ChatGPT |
| Schizophrenia | Elomia, ChatGPT |
How Do They Work?
Mental health chatbots operate on principles of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
They are trained on vast datasets of therapeutic conversations and are capable of learning from user interactions to improve over time. This article explores the science behind AI in mental health in detail.
Their operation involves:
- User Interaction: Users initiate a conversation by typing or speaking.
- Processing: The chatbot processes the input, often employing Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the context.
- Response Generation: Based on the input, the chatbot generates a response, which can include advice, information, or further questions to understand the user better.
- Feedback Loop: Some chatbots have a feedback loop allowing users to rate the helpfulness of responses, which in turn helps the chatbot learn and improve.
These digital companions are revolutionizing the way we seek support for mental health issues, bridging the gap between individuals and mental health resources.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their potential, AI chatbots face challenges including:
- Difficulty in understanding complex human emotions
- Lack of personal touch
- Privacy concerns
These hurdles hint at the need for human oversight and the importance of combining digital and human support for optimal mental health care.
Exploration of Popular Mental Health Chatbots
Diving into the world of AI chatbots for mental health unveils a variety of digital companions, each with unique strengths and weaknesses.
Woebot
Woebot is your friendly AI companion making mental health care accessible.
- Features: Mood tracking, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) based conversations, and personalized mental health resources.
- Strengths: Proven effectiveness, user-friendly, based on established psychological principles.
- Weaknesses: Limited to text interactions, may not interpret emotions accurately.
Youper
Youper, a multi-faceted mental health chatbot, boasts diverse therapeutic approaches.
- Features: Emotion identification, mindfulness practices, and therapy exercises.
- Strengths: Variety of therapeutic approaches, user-friendly interface.
- Weaknesses: Subscription fee for full access, may lack the personal touch of human interaction.
Elomia
Elomia provides a comforting space for individuals facing emotional challenges.
- Features: Real-time conversations, emotional support, and mental well-being exercises.
- Strengths: Hyper-realistic conversations, high user satisfaction.
- Weaknesses: Limited information on effectiveness, may not replace professional therapy.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT offers a broad spectrum of supportive conversations.
- Features: Guided conversations, information provision on mental health issues.
- Strengths: Wide range of topics, advanced language processing capabilities.
- Weaknesses: Cannot replace professional therapy, may not understand complex emotions.
Earkick
Earkick focuses on mood enhancement through personalized recommendations.
- Features: Activity recommendations, mood tracking, real-time conversations.
- Strengths: Data-driven recommendations, engaging user interface.
- Weaknesses: May lack depth in therapeutic approaches, subscription fee for full access.
Each of these chatbots, with their unique offerings, is pushing the boundaries in providing mental health support, making therapy more accessible and less stigmatized.
The Science Behind AI Chatbots
Unveiling the scientific principles that drive these digital companions.
Psychological Frameworks
Chatbots often employ established psychological frameworks like:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
- Mindfulness
Technical Foundations
AI chatbots operate on cutting-edge technologies:
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
| Technology | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Machine learning (ML) | ML is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms are used to train chatbots to understand and respond to user input in a meaningful way. | Woebot uses ML to generate personalized CBT interventions for users. |
| Natural language processing (NLP) | NLP is a field of AI that deals with the interaction between computers and human (natural) languages. NLP algorithms are used to train chatbots to understand and generate human language. | Youper uses NLP to understand the user’s emotional state and provide tailored support. |
| Artificial intelligence (AI) | AI is a broad field of computer science that deals with the creation of intelligent agents, which are systems that can reason, learn, and act autonomously. AI algorithms are used to power chatbots and give them the ability to understand and respond to user input in a meaningful way. | Elomia uses AI to provide personalized support for a variety of mental health issues. |
| Chatbot platform | A chatbot platform is a software platform that provides the tools and infrastructure needed to develop and deploy chatbots. Chatbot platforms typically include features such as natural language processing, machine learning, and dialogue management. | ChatGPT is a chatbot platform that allows developers to create and deploy AI chatbots that can be used for a variety of purposes, including mental health support. |
Training and Learning
Chatbots are trained on vast datasets and continually learn from user interactions. Explore the interplay of AI and mental health for a deeper understanding.
Effectiveness
Studies show varying degrees of effectiveness, with some users finding substantial support while others feel the lack of human touch.
Each technological and psychological element plays a crucial role in enhancing the support provided by AI chatbots in the mental health domain.
Benefits of Using AI Chatbots for Mental Health
The digital era brings forth innovative solutions for mental health.
Accessibility
- 24/7 Availability: Chatbots are available round the clock, providing support whenever needed.
- Global Reach: They transcend geographical boundaries, making mental health support accessible globally.
Affordability
- Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper than traditional therapy.
- Free Versions: Some chatbots offer free versions with valuable features.
Anonymity
- Privacy: Users can remain anonymous, promoting openness and honesty.
- Stigma-Free: Provides a stigma-free environment for discussing mental health.
| Cost | AI Chatbot | Traditional Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront cost | High | Low |
| Ongoing cost | Low | High |
| Cost over time | Decreasing | Increasing |
These benefits, as discussed in this article, highlight the potential of AI chatbots in making mental health care more accessible, affordable, and stigma-free.
Concerns and Ethical Implications
Despite the advancements, there are concerns surrounding AI chatbots in mental health.
Privacy and Data Security
- Data Handling: How chatbots handle sensitive information is crucial.
- Consent: Ensuring informed consent before collecting user data.
Effectiveness
- Therapeutic Relationship: Lack of human touch could affect the therapeutic relationship.
- Misinterpretation: Risk of misinterpreting user input leading to incorrect advice.
Regulatory Oversight
- Standardization: Lack of standardization in chatbot responses.
- Professional Oversight: Need for professional oversight to ensure accurate and ethical responses.
Each concern underscores the importance of a well-rounded approach, combining AI with human expertise as explored in this article.
The Future of AI Chatbots in Mental Health
The horizon is promising with the continual evolution of AI technologies.
Potential Developments
- Enhanced emotion recognition
- Improved personalization
- Integration with other digital health tools
Evolving Ethical Standards
- Stricter data privacy regulations
- Standardization of chatbot responses
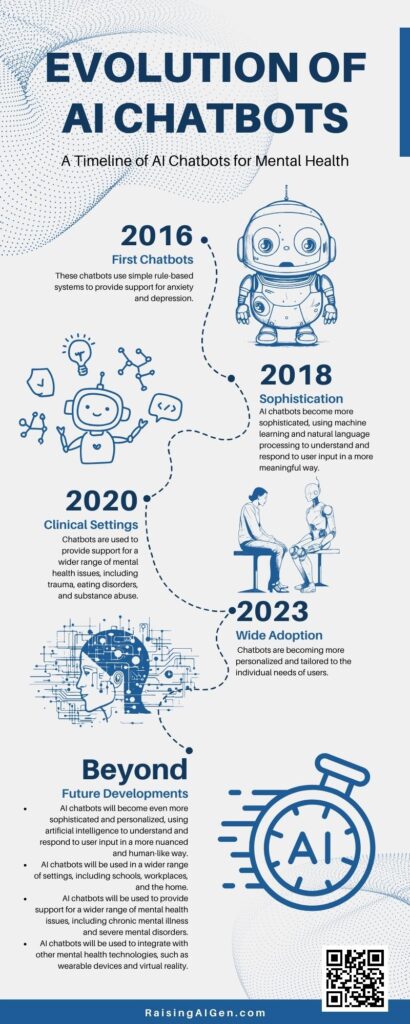
The synergy of technology and mental health opens up vast possibilities as elaborated in this article.
Navigating the Digital Therapeutic Landscape
As we venture into the heart of digital transformation, AI chatbots emerge as a beacon of support in the often tumultuous seas of mental health.
They promise a world where help is just a click away, devoid of judgment, waiting to assist us in our moments of need. Although they may never replace the warm reassurance of human interaction, their potential to augment support is undeniable.
As we continue to fine-tune the algorithms and address the ethical quandaries, the future holds a promise of a more supportive digital landscape, always accessible, always ready to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
| Question | Answer |
| What are AI chatbots for mental health? | AI chatbots for mental health are digital platforms designed to provide support and coping strategies for individuals facing mental health challenges. |
| How do AI chatbots work? | They operate on principles of AI and machine learning, processing user input to provide personalized responses. |
| Are AI chatbots effective for mental health support? | They can provide valuable support, but effectiveness may vary and they should not replace professional therapy. |
| Are AI chatbots safe to use? | While generally safe, privacy concerns around data handling do exist. |
| Can AI chatbots replace human therapists? | No, they are designed to augment, not replace, human therapists. |
| What are some popular mental health chatbots? | Woebot, Youper, Elomia, ChatGPT, and Earkick are some examples. |